策略模式
定义
定义一簇算法类,将每个算法分别封装起来,让他们可以互相替换,策略模式可以使算法的变化独立于使用它们的客户端
场景
使用策略模式,可以避免冗长的if-else 或 switch分支判断
实现
策略的定义
策略的定义需要定义一个策略接口和一组实现这个接口的策略类,因为所有的策略类都实现相同的接口
public interface Strategy{ void algorithm();}public class ConcreteStrategyA implements Strategy { @Override public void algorithm() { //具体的算法... }}public class ConcreteStrategyB implements Strategy { @Override public void algorithm() { //具体的算法... }}策略的创建
在使用的时候,一般会通过类型来判断创建哪个策略来使用,在策略上下文中,可以使用map维护好策略类
策略的使用
策略模式包含一组可选策略,在使用策略时,一般如何确定使用哪个策略呢?最常见的是运行时动态确定使用哪种策略。程序在运行期间,根据配置、计算结果、网络等这些不确定因素,动态决定使用哪种策略
public class StrategyContext{ private static final Map<String, Strategy> strategies = new HashMap<>(); static { strategies.put("A", new ConcreteStrategyA()); strategies.put("B", new ConcreteStrategyB()); } private static Strategy getStrategy(String type) { if (type == null || type.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("type should not be empty."); } return strategies.get(type); } public void algorithm(String type){ Strategy strategy = this.getStrategy(type); strategy.algorithm(); }}UML
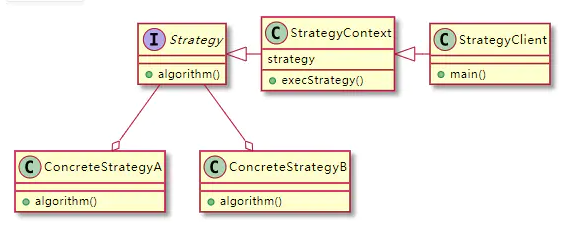
策略模式的创建和使用--Spring和自定义注解
在介绍策略模式时,在上下文中使用了map存储好的策略实例,在根据type获取具体的策略,调用策略算法。
当需要添加一种策略时,需要修改context代码,这违反了开闭原则:对修改关闭,对扩展开放。
要实现对扩展开放,就要对type和具体的策略实现类在代码中进行关联,可以使用自定义注解的方式,在注解中指定策略的type。
策略上下文实现类实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口,在该接口中编写策略类型与bean的关系并维护到策略上下文中。
package com.masterlink.strategy;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;import org.springframework.core.Ordered;import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Set;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;@Slf4j@Componentpublic class StrategyDemoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered { private final Set<Class<?>> nonAnnotatedClasses = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64)); private final StrategyContext strategyContext; private StrategyDemoBeanPostProcessor(StrategyContext context) { this.strategyContext = context; } @Override public int getOrder() { return LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException { if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(bean.getClass())) { // 获取使用 @StrategyDemo 注解的Class信息 Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean); Class<Strategy> orderStrategyClass = (Class<Strategy>) targetClass; StrategyDemo ann = findAnnotation(targetClass); if (ann != null) { processListener(ann, orderStrategyClass); } } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } protected void processListener(StrategyDemo annotation, Class<Strategy> classes) { // 注册策略 this.strategyContext .registerStrategy(annotation.type(), classes); } private StrategyDemo findAnnotation(Class<?> clazz) { StrategyDemo ann = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(clazz, StrategyDemo.class); return ann; }}@Componentpublic class StrategyContext implements ApplicationContextAware { private final Map<String, Class<Strategy>> strategyClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); private final Map<String, Strategy> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); private ApplicationContext applicationContext; /** * 注册策略 * @param type * @param strategyClass */ public void registerStrategy(String type, Class<Strategy> strategyClass){ if (strategyClassMap.containsKey(type)){ throw new RuntimeException("strategy type:"+type+" exist"); } strategyClassMap.put(type, strategyClass); } /** * 执行策略 * @param type */ public void algorithm(String type){ Strategy strategy = this.getStrategy(type); strategy.algorithm(); } private Strategy getStrategy(String type) { if (type == null || type.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("type should not be empty."); } Class<Strategy> strategyClass = strategyClassMap.get(type); return createOrGetStrategy(type, strategyClass); } private Strategy createOrGetStrategy(String type,Class<Strategy> strategyClass ){ if (beanMap.containsKey(type)){ return beanMap.get(type); } Strategy strategy = this.applicationContext.getBean(strategyClass); beanMap.put(type, strategy); return strategy; } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; }}实用案例
在我们的平台中,有一部分是使用的netty框架编写的tcp服务,在服务端,需要将二进制转换为对象,在协议设计阶段,定义第一个字节表示对象类型,比如int,String等,第二三个字节,表示数据长度,后面的字节位传输内容。
比如,
0x01, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x09,解析出来的内容是int类型数字9。
0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 解析出的内容是String类型,内容是 123。
在不使用策略模式的时候,需要将第一个字节解析出来,然会使用if--else判断类型,对后继的字节进行解析。
在实际的实现过程中,是使用了策略模式,并且使用注解的方式表示数据类型,实现过程如下。
定义策略接口和注解
定义 CodecStrategyType 注解和编码解码器的策略接口 CodecStrategy
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface CodecStrategyType { /** * 编码解码类型 * @return */ byte type();}public interface CodecStrategy<T> { T decoding(byte[] buffer);}/** 通用解码接口 */public interface Codec { Object decoding(byte[] bytes);}策略实现
实现两种类型的解码器: Integer 和 String
/** * integer解码 */@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte)0x01)@Servicepublic class IntgerCodecStrategy implements CodecStrategy<Integer> { @Override public Integer decoding(byte[] buffer) { int value; value = (int) ((buffer[3] & 0xFF) | ((buffer[2] & 0xFF)<<8) | ((buffer[1] & 0xFF)<<16) | ((buffer[0] & 0xFF)<<24)); return value; }}@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte)0x02)@Servicepublic class StringCodecStrategy implements CodecStrategy<String> { @Override public String decoding(byte[] bufferr) { return new String(bufferr); }}策略上下文和策略注册
策略上下文类 CodecStrategyContext 提供了统一解码入口,将 byte[] 转换为 Object 类型,同时提供策略的注解接口 void registerStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass) ,注册解码类型对应的策略实现类。
策略上下文类同时还提供了策略Bean的创建,根据类型从Spring 的 ApplicationContext 获取策略bean,并缓存到map。
策略Bean处理类 CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor 中解析 CodecStrategyType 注解中指定的类型。
@Componentpublic class CodecStrategyContext implements ApplicationContextAware, Codec { private final Map<Byte, Class<CodecStrategy<?>>> strategyClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); private final Map<Byte, CodecStrategy<?>> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); private ApplicationContext applicationContext; /** * 注册策略 * @param type * @param strategyClass */ public void registerStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass){ if (strategyClassMap.containsKey(type)){ throw new RuntimeException("strategy type:"+type+" exist"); } strategyClassMap.put(type, strategyClass); } /** * 执行策略 */ @Override public Object decoding(byte[] bytes){ Byte type = bytes[0]; CodecStrategy<?> strategy =this.getStrategy(type); byte l1 = bytes[1]; byte l2= bytes[2]; short length = (short) ((l2 & 0xFF) | ((l1 & 0xFF)<<8)); byte[] contentBytes = new byte[length]; arraycopy(bytes,3,contentBytes,0, length); return strategy.decoding(contentBytes); } private CodecStrategy<?> getStrategy(Byte type) { Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass = strategyClassMap.get(type); return createOrGetStrategy(type, strategyClass); } private CodecStrategy<?> createOrGetStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass ){ if (beanMap.containsKey(type)){ return beanMap.get(type); } CodecStrategy<?> strategy = this.applicationContext.getBean(strategyClass); beanMap.put(type, strategy); return strategy; } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; }}@Componentpublic class CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered { private final Set<Class<?>> nonAnnotatedClasses = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64)); private final CodecStrategyContext strategyContext; private CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor(CodecStrategyContext context) { this.strategyContext = context; } @Override public int getOrder() { return LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException { if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(bean.getClass())) { // 获取使用 @StrategyDemo 注解的Class信息 Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean); Class<CodecStrategy<?>> orderStrategyClass = (Class<CodecStrategy<?>>) targetClass; CodecStrategyType ann = findAnnotation(targetClass); if (ann != null) { processListener(ann, orderStrategyClass); } } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } protected void processListener(CodecStrategyType annotation, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> classes) { // 注册策略 this.strategyContext .registerStrategy(annotation.type(), classes); } private CodecStrategyType findAnnotation(Class<?> clazz) { CodecStrategyType ann = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(clazz, CodecStrategyType.class); return ann; }}使用和测试
测试Integer和String类型的策略:
- 0x01, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x09,解析出来的内容是int类型数字9。
- 0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 解析出的内容是String类型,内容是 123。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)@ContextConfiguration(classes = {CodecStrategyTest.CodecStrategyTestConfig.class})public class CodecStrategyTest { @Resource Codec codec; @Test public void testInterDecoding(){ byte[] buffer = new byte[]{ 0x01,0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00,0x00, 0x09 }; Integer decoding = (Integer)codec.decoding(buffer); assertThat(decoding) .isNotNull() .isEqualTo(9); } @Test public void testStringDecoding(){ byte[] buffer = new byte[]{ 0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32,0x33 }; String decoding = (String)codec.decoding(buffer); assertThat(decoding) .isNotNull() .isEqualTo("123"); } @ComponentScan({"com.masterlink.strategy"}) @Configuration public static class CodecStrategyTestConfig { }}扩展复杂类型
自定义复杂类型User类,对应协议类型为 0xA0, 第2 、3 字节表示整个对象的字段长度,紧接着是 Integer 类型的age 和 String 类型的name,
比如 0xA0, 0x00 0x10 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x17, 0x00, 0x08, 0x5A,0x68,0x61,0x6E,0x67,0x53, 0x61,0x6E, 对应的user对象是
{ "age": 23, "name": "ZhangSan"}@Datapublic class User { private Integer age; private String name;}实现解码策略类
已知 User 中的基础类型依赖了 Integer 和 String ,所以在User的解码策略类中,依赖了 IntgerCodecStrategy 和 StringCodecStrategy
@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte) (0xA0))@Servicepublic class UserCodeStrategy implements CodecStrategy<User> { private final StringCodecStrategy stringCodecStrategy; private final IntgerCodecStrategy intgerCodecStrategy; public UserCodeStrategy(StringCodecStrategy stringCodecStrategy, IntgerCodecStrategy intgerCodecStrategy) { this.stringCodecStrategy = stringCodecStrategy; this.intgerCodecStrategy = intgerCodecStrategy; } @Override public User decoding(byte[] buffer) { byte ageL1 = buffer[0]; byte ageL2 = buffer[1]; short ageLength = (short) ((ageL2 & 0xFF) | ((ageL1 & 0xFF)<<8)); byte[] ageBytes = new byte[ageLength]; System.arraycopy(buffer,2, ageBytes,0,ageLength); byte nameL1 = buffer[0+ageLength]; byte nameL2 = buffer[1+ageLength]; short nameLength = (short) ((nameL2 & 0xFF) | ((nameL1 & 0xFF)<<8)); byte[] nameBytes = new byte[nameLength]; System.arraycopy(buffer,2+ageLength+2, nameBytes,0,nameLength); User user = new User(); user.setAge(intgerCodecStrategy.decoding(ageBytes)); user.setName(stringCodecStrategy.decoding(nameBytes)); return user; }}测试
通过测试可以发现很轻松的就扩展了一个复杂类型的解码算法,这样随着协议的增加,可以做到对修改代码关闭,对扩展代码开放,符合开闭原则。
@Test public void testUserDecoding(){ byte[] buffer = new byte[]{ (byte)0xA0, (byte)0x00 ,(byte)0x10 ,(byte)0x00, (byte)0x04, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x17, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x08, (byte)0x5A, (byte)0x68, (byte)0x61, (byte)0x6E, (byte)0x67, (byte)0x53, (byte)0x61, (byte)0x6E }; User user = (User)codec.decoding(buffer); assertThat(user) .isNotNull(); assertThat(user.getAge()).isEqualTo(23); assertThat(user.getName()).isEqualTo("ZhangSan"); }总结
- 使用策略模式,可以避免冗长的if-else 或 switch分支判断
- 掌握自定义注解的是使用方式
- 与使用
@Service("name")注解相比,自定义注解方式支撑和扩展的类型或更灵活
关注我的公众号,一起探索新知识新技术

原文转载:http://www.shaoqun.com/a/756807.html
三维度科技:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1312
徐家骏:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1803
策略模式定义定义一簇算法类,将每个算法分别封装起来,让他们可以互相替换,策略模式可以使算法的变化独立于使用它们的客户端场景使用策略模式,可以避免冗长的if-else或switch分支判断实现策略的定义策略的定义需要定义一个策略接口和一组实现这个接口的策略类,因为所有的策略类都实现相同的接口publicinterfaceStrategy{ voidalgorithm();}publicclassCo
logo免费制作:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1998
拍拍网:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2205
斑马物流:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1316
为了丈夫我牺牲了自己 口述在酒店和暴躁总裁的交易:http://lady.shaoqun.com/a/269722.html
口述:离婚前我被闺蜜"劫持":http://lady.shaoqun.com/a/272633.html
货运压力大!日本空运暂停,国内华南港口还未恢复!:https://www.ikjzd.com/articles/6905
No comments:
Post a Comment